Orca Slicer Wiki | Print settings, Calibration, Support Structures
Welcome to the Orca Slicer Wiki, your comprehensive, go-to resource for mastering one of the most powerful free and open-source 3D printing slicers available today. Whether you’re a complete beginner taking your first steps in 3D printing, or an experienced user switching from another slicer and looking to harness advanced features, this guide is built for you.
We cover everything from initial setup, printer and material profiles, process tuning, and calibration right through to troubleshooting and expert workflows – helping you configure Orca Slicer for reliable, high-quality prints without the frustration. Let’s dive in and make your printing journey smoother than ever.
Getting Started
Download & Installation
If you’re ready to dive into Orca Slicer, the first step is the orca slicer download. Orca Slicer is free and open-source (licensed under the GNU AGPL) and available for Windows, macOS and Linux.
Here’s what you need to know about installation and system compatibility:
- Systems supported: Windows (64-bit), macOS (Intel/Apple Silicon), Linux (AppImage/flatpak).
- Minimum system requirements: Generally, at least 4 GB RAM is needed, though 8 GB or more is recommended. Graphics should support OpenGL or equivalent.
- Installation flow: Download the installer for your platform, run the setup (or, on Linux, make the AppImage executable). Once installed, the first-run wizard helps you select your printer model from the list of orca slicer supported printers or set up a custom profile.
- Safe download tips: Always use the official site or the GitHub releases page for Orca Slicer versions (e.g., v2.3.1).
By the end of this step you’ll have Orca Slicer installed and ready, now you’re set to move on to picking your printer profile and slicing your first model.
Interface Overview
Once the software is installed and running, you’ll be greeted by the Orca Slicer interface, which is designed around a streamlined workflow: Printer → Filament → Process.
Here’s what to expect:
- Sidebar / Preset selectors: Choose your printer model (or custom setup), select a filament profile (or import one via orca slicer filament profiles download), then pick a process preset (e.g., quality, strength, speed).
- 3D Preview / Bed View: The main viewport shows your build plate, model(s) positioned, supports preview and layer look-through.
- Toolbar / Menu: Access File, Settings, Print Setup, Preview, Export. The slicer toolbar allows toggling between simple or advanced view modes.
- Workflow: After selecting printer → filament → process, you slice the model, examine the preview for walls/infill/supports, then export the G-code to send to your 3D printer.
- Links for deeper tour: See our separate sub-page “Interface Tour” for annotated screenshots and UI walkthroughs.
Profiles & Presets
One of the major strengths of Orca Slicer is its rich profiles system making it easier for both beginners and advanced users to dial in prints quickly. Here’s how it breaks down:
- Printer Profile: This defines your 3D printer’s build volume, nozzle size, firmware type (Marlin, Klipper, etc.), number of extruders and other machine-specific parameters. Picking the correct profile from the built-in list (or creating a custom one) ensures correct g-code output and compatibility with your printer.
- Filament Profile (Material Profile): These control nozzle & bed temperature, cooling fan behaviour, flow multiplier, retraction, etc. Many users engage in orca slicer filament profiles download to import vendor-approved or community-tuned profiles for specific materials (PLA, PETG, ABS, TPU).
- Process Profile (Print Settings): This covers the print settings such as layer height, infill pattern/density, wall thickness, speed/acceleration, support strategy. Built-in presets give a good starting point; you can then tune them for your machine and material to create a “tuned” setup rather than just stock.
- Built-in vs Custom:
- Built-in (stock) profiles are pre-configured for typical machines/materials and are safe starting points for beginners.
- Tuned/Custom profiles are where you refine values (for instance optimal print speed for your specific printer and filament) useful for experienced users who want the best quality or speed.
- Why it matters: Using correct profiles dramatically reduces tuning time, lowers failed prints, minimizes material waste and makes your switch to Orca Slicer smoother especially if you are coming from another slicer.
Supported Operating Systems and Printers
| Platform | Supported Versions | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | 10, 11 (64-bit) | Most stable, full GPU acceleration |
| macOS | 12.0+ | Optimized for Apple Silicon (M1/M2) |
| Linux | Ubuntu, Fedora, Arch | Uses AppImage or .deb builds |
| Printers | Bambu Labs, Creality, Ender 3, Anycubic, Prusa, Voron, etc. | Fully configurable profiles |
Once you’ve completed this “Getting Started” phase – installed Orca Slicer, familiarized yourself with the interface, loaded the correct profiles, you’re ready for the next major step: Printer Setup & Profiles, where we dive deep into machine-specific settings, tuning and the list of supported printers.
Printer Setup & Profiles
Printer Settings in Orca Slicer
Proper printer configuration in Orca Slicer is essential for achieving fast, high-quality, and damage-free prints. This section covers all critical printer settings and helps you fine-tune them for the best results—whether you’re using a Bambu Lab, Ender 3, Prusa, or any other FDM printer.
Air Filtration / Exhaust Fan Handling
If your 3D printer has external air filters or exhaust fans designed to remove VOCs (volatile organic compounds) or UFPs (ultrafine particles) from the print chamber, Orca Slicer allows you to control them natively.
You can toggle these fans automatically during printing using G-code commands or custom macros, ensuring clean air management and reducing odor or particle buildup.
Key Features:
- Manage external air filters or exhaust fans directly via Orca commands
- Remove VOCs and UFPs automatically during prints
- Configure fan speeds per material or print stage
- Create custom macros to turn fans on/off based on layer or temperature
Pro Tip:
Use the Exhaust Fan Speed setting under Printer → Cooling → Air Filtration to synchronize fan operation with temperature or print time.
Read more: [Air Filtration / Exhaust Fan Control]
Auxiliary Fan Settings
Auxiliary fans play a crucial role in maintaining consistent cooling of the freshly extruded filament, particularly during bridging or overhangs. Incorrect fan settings can cause warping, sagging, or uneven layer adhesion.
In Orca Slicer, you can:
- Adjust fan speed curves by material type (PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, etc.)
- Enable smart fan ramping for layer transitions
- Control fan acceleration/deceleration between layers
- Sync auxiliary fans with nozzle temperature changes
- Prevent print flaws like warping, drooping, and inconsistent layer bonding
- Automatically shut off cooling fans post-print to protect electronics
Navigate to Cooling → Auxiliary Fan to define fan behavior per filament or print stage.
Read more: [Auxiliary Fan Settings]
Chamber Temperature Control
Temperature stability inside the print chamber can make or break a print, especially with materials like ABS, ASA, or Nylon. Orca Slicer includes Chamber Temperature Control commands that help you maintain optimal thermal conditions without external sensors.
Key Benefits:
- Maintain consistent print chamber heat for high-temp materials
- Enable automatic preheat before printing
- Link chamber temperature to bed and nozzle temps
- Prevent cracking or warping in large ABS/ASA models
- Preset temperature profiles by filament type
- PID-based regulation through printer G-code macros
You can access this under Printer Settings → Temperature → Chamber Control.
Read more: [Chamber Temperature Control]
Adaptive Bed Mesh (ABL)
The Adaptive Bed Mesh feature helps you map and compensate for surface unevenness on your print bed. Orca Slicer supports both manual mesh leveling and automatic bed leveling (ABL) routines compatible with firmware like Marlin, Klipper, and RepRap.
Why It Matters:
- Auto-compensate for uneven print surfaces
- Supports BLTouch, CR-Touch, and inductive sensors
- Save mesh profiles for multiple beds or materials
- Ensures perfect first-layer adhesion
- Reduces warping or bed detachment
- Improves dimensional accuracy for tall prints
You can enable this from Printer → Bed Leveling → Adaptive Mesh. Orca can also integrate with sensors like BLTouch or CR-Touch for dynamic adjustments.
Read more: [Adaptive Bed Mesh]
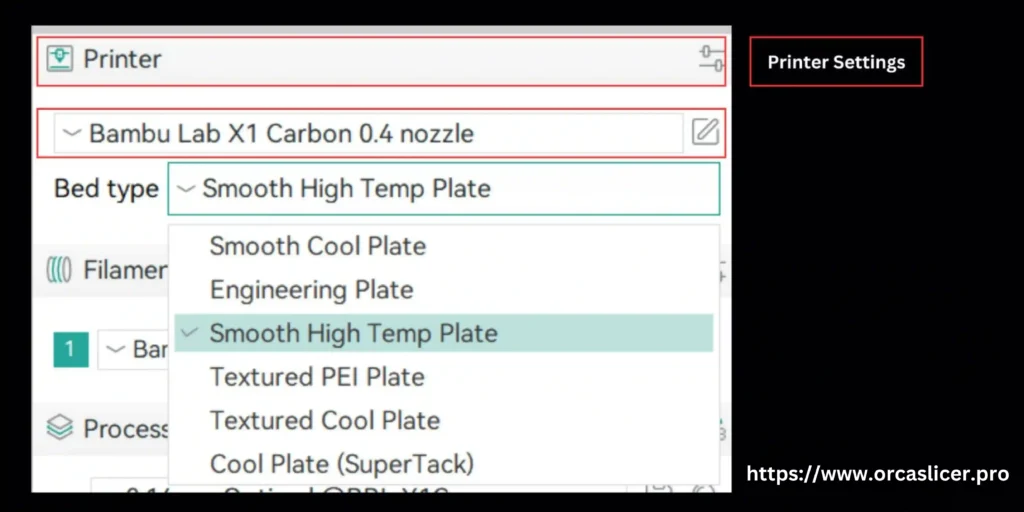
Multiple Bed Type Settings
Orca Slicer supports multiple print bed types — from PEI and glass to flex steel or magnetic sheets. Each bed type has unique thermal behavior, so configuring them correctly is key for reliability and adhesion.
Configuration Options:
- Create profiles for glass, PEI, and magnetic beds
- Assign different adhesion and temperature values per bed
- Store reusable presets for material-specific beds
- Prevent first-layer shift caused by inconsistent surfaces
- Adjust first-layer height and flow rate per bed
- Save temperature presets for quick switching between surfaces
Access via Printer → Bed Type Settings to switch between saved configurations easily.
Read more: [Setting Multiple Bed Types]
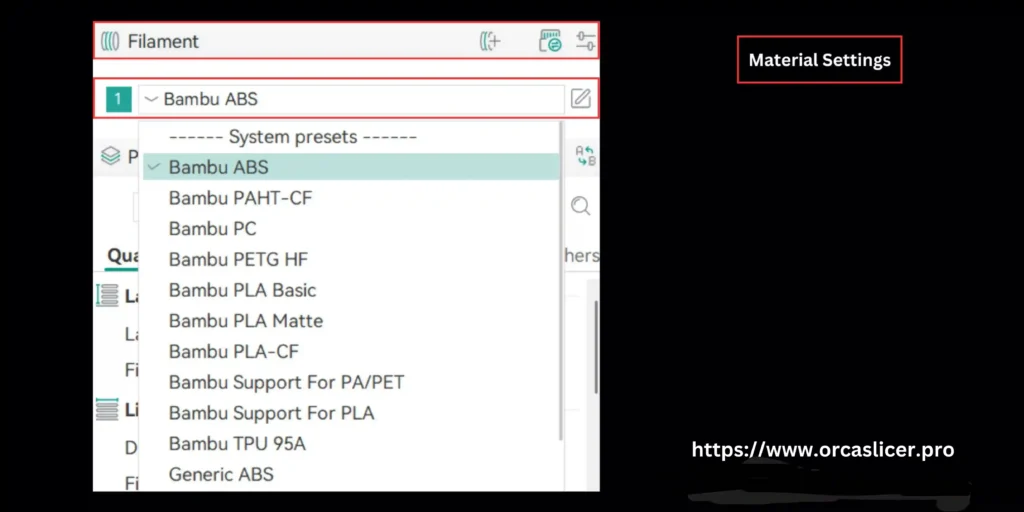
Material Settings
In 3D printing, material configuration is one of the most important steps in achieving accurate, durable, and visually perfect prints. Each filament or material type whether PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, Nylon, or composites requires unique adjustments for print speed, temperature, cooling, adaptive bed mesh, and bed adhesion. Incorrect material settings can result in failed prints, nozzle clogs, or even hardware damage.
Orca Slicer simplifies this process with pre-configured profiles, material wizards, and full customization options to match your project’s needs.
By the end of this step you’ll have Orca Slicer installed and ready, now you’re set to move on to picking your printer profile and slicing your first model.
Single Extruder Multimaterial
When printing with multiple materials using a single extruder, Orca Slicer offers specialized settings to maintain quality, prevent cross-contamination, and manage temperature transitions.
Key configurations include:
- Prime Tower Setup: Define position, size, and temperature of the prime tower for stable filament switching.
- Ramming Settings: Control extrusion retraction speed during filament change to prevent stringing or clogging.
- Filament Change Temperature: Adjust nozzle temperature dynamically between materials (e.g., from PLA to PETG).
- Color and Material Switching Speed: Manage speed transitions for multi-color or multi-material models.
- Filament Cooling Synchronization: Automatically calibrate fan speeds after filament swaps to maintain layer consistency.
Read more: [Single Extruder Multimaterial]
Pellet Printers (Pellet Flow Coefficient)
For large-scale or industrial 3D printing, pellet extruders replace standard filament spools. These machines use granulated plastic pellets that are melted and extruded through a high-capacity nozzle.
Because pellet flow is measured differently than filament, Orca Slicer provides pellet flow coefficient settings to calculate extrusion volume precisely.
Key things to configure:
- Flow Coefficient Calibration: Replace volume-based extrusion with mass or flow-based calibration.
- Material Type Recognition: Adjust settings for different pellet types (ABS, PLA, PC, etc.) to maintain optimal viscosity.
- Hopper Temperature Control: Manage pre-heating and drying for moisture-sensitive pellets.
- Screw Feed Rate: Fine-tune extrusion pressure and material throughput.
- Cooling System Integration: Sync external coolers or chamber fans to stabilize pellet melting temperature.
Understanding these distinctions helps you achieve filament-quality precision even in high-volume pellet printing.
Read more: Pellet Printers (Pellet Flow Coefficient)]
Process Settings
Once your printer, material, and speed configurations are complete, the next step is defining your Process Settings. These determine how every aspect of the print—quality, speed, walls, and precision—is controlled during execution. Proper process calibration ensures smooth surfaces, strong layers, and consistent results across all print types.
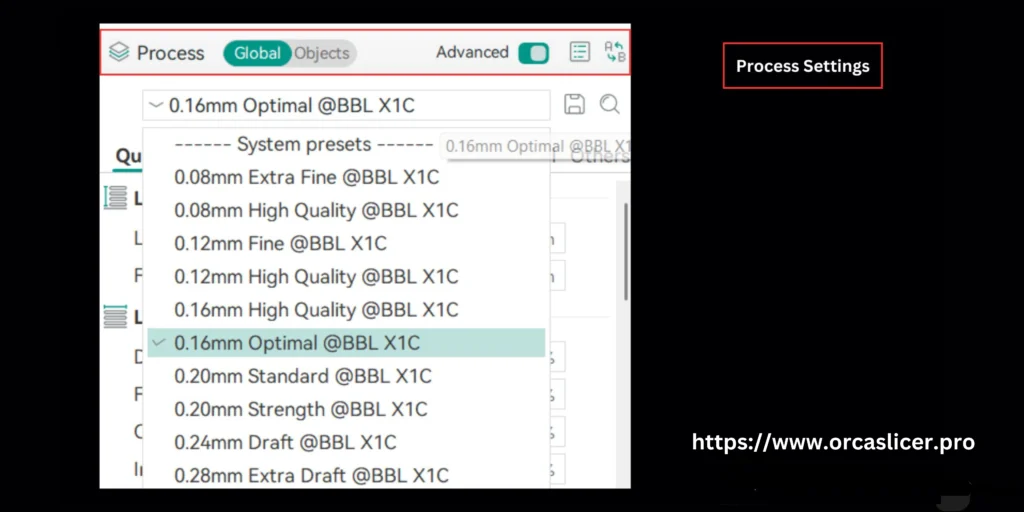
Orca Slicer provides a comprehensive toolkit for managing each of these parameters step-by-step.
Quality Settings
Quality settings define the aesthetic and mechanical outcome of your print. Each small parameterlayer height, line width, seams, and precision plays a vital role in the final look and durability.
Layer Height
Lower heights = finer detail but longer print times. Ideal for display models or parts requiring precision.
Read more: [Layer Height Settings]
Line Width:
Adjust the extrusion width in millimeters or as a percentage of nozzle diameter for consistent wall thickness.
Read more: Line Width Settings
Seam Control
Manage start/end points to minimize visible lines and ensure a clean surface finish.
Read more: [Seam Settings]]
Precision Settings
Fine-tune arc fitting, XY dimensional accuracy, gap closing, and Z-height corrections. These tools help maintain engineering tolerances, prevent dimensional drift, and improve fit for mechanical and functional parts.: Fine-tune arc fitting, XY dimensional accuracy, gap closing, and Z-height corrections are under process setting tab.
Read more: Precision Settings
Ironing Settings
Smooth out the top surface by reprinting the topmost layer at reduced speed for a polished finish. Smooth out the top surface by reprinting the topmost layer at reduced speed for a polished finish. Control ironing flow, spacing, pattern type, and number of passes to eliminate micro-gaps and produce ultra-smooth top layers
Read more: IroningSettings
Strength Settings
While dimensional accuracy and aesthetic finish are important, the structural strength, durability, and load-bearing performance of a 3D print are equally critical especially for functional parts, mechanical components, or high-stress applications.
Orca Slicer gives you deep control over the internal and external structure of your print, allowing you to tune factors such as wall thickness, shells, infill patterns, and advanced mechanical behavior.
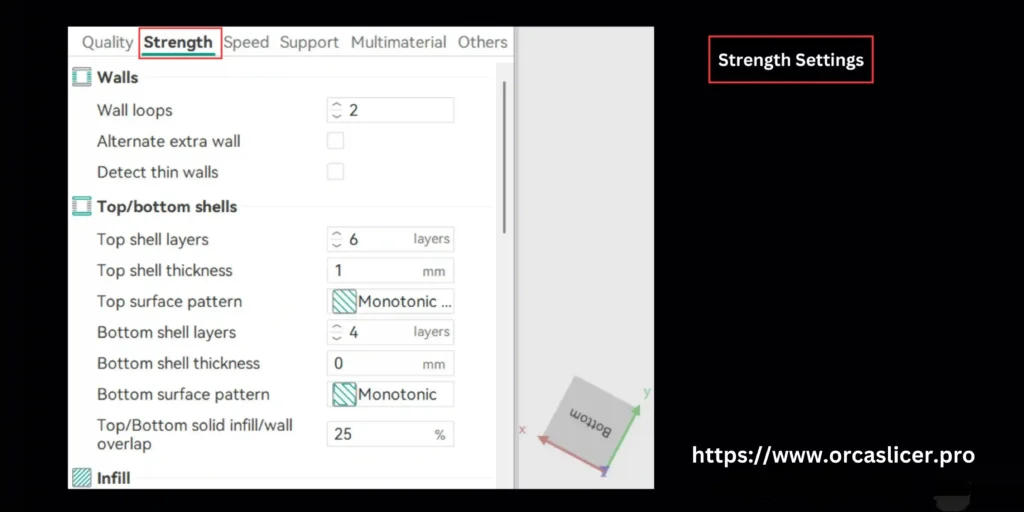
This section explains how each setting contributes to part strength and how to configure them for different print goals.
Walls
Walls are the outer “shell” or perimeters that define the structural frame of your print. Increasing the number and type of walls drastically improves durability, surface hardness, and impact resistance.
What You Can Control
- Structural Integrity Check: Automatically detects fragile wall features and compensates.
- Wall Loops: Add multiple outer perimeters to strengthen load-bearing surfaces
- Thin Wall Detection: Prevents thin features from collapsing by “expanding” or “reconstructing” wall paths.
- Extra Walls on Overhangs: Automatically add reinforcement where the print might otherwise sag.
- Wall Ordering: Choose whether the outer or inner wall prints first for strength vs. surface quality.
- Wall Transition Speed: Adjusts extrusion behavior at corners to reduce weak points.
Line Width:
These are the solid layers that seal the infill and give your part rigidity. Incorrect shell settings often cause weak tops, fragile bottoms, or cracking.
What You Can Configure
- Gap Fill Logic (controls tiny voids under the surface)
- Shell Thickness (number of layers or direct mm value)
- Surface Patterns (rectilinear, monotonic, concentric, aligned)
- Surface Density (how solid the top/bottom should be)
- Infill/Wall Overlap (critical for bonding shells to infill)
- Solid Layer Expansion (reinforces thin or small areas)
Read more: Line Width Settings
Infill
Infill is the internal structure that supports walls and distributes mechanical stress. The right infill dramatically changes the part’s behavior.
Adjustable Infill Parameters
- Infill Speed (slower = better adhesion).
- Infill Density (overall strength percentage)
- Gap Fill Application (prevents hollow spots that weaken layer bonding)
- Multiline Overlap (controls how strongly infill bonds to walls)
- Tiny Gap Filtering (removes small voids that reduce strength)
- Anchor Settings (reinforce infill where it meets shells)
Fill Patterns
Infill pattern determines how load is distributed inside the print. Pattern affects strength, flexibility, rigidity, and print time.
Common Patterns & Their Behavior
- Lightning → Fastest, weakest (not for functional parts)
- Gyroid → Best overall strength + flexibility + all-direction support
- Cubic → Extremely strong for load-bearing structures
- Grid → Fast to print, moderate strength
- Triangular / Tri-Hexagon → High rigidity, excellent for mechanical parts
- Concentric → Good for flexible print
Template Metalanguage for Infill Rotation
This advanced system allows you to set the infill rotation logic using template-based instructions.
What You Can Define
- Mechanical stress-oriented infill behavior
- Angle for each layer
- Rotational increment for multi-layer infills
- Custom sequencing logic
- Conditional rules for specific layer numbers
- Model-aligned infill directions
Advanced Strength Settings
These advanced configurations help push your print’s structural performance further.
What You Can Control
- Align Infill to Model Geometry
Improve strength by matching infill direction with real-world stress lines. - Bridge Infill Direction
Ensures infill prints cleanly over gaps without sagging. - Sparse Infill Threshold
Prevents weak internal areas by auto-reinforcing thin regions. - Detect Narrow Internal Solid Infill
Keeps small internal structures solid instead of hollow, increasing durability. - Infill/Wall Bonding Enhancements
Improves how internal structures fuse with external walls.
Best For
- Industrial parts
- Engineering polymers
- High-heat materials
- High-stress or load-bearing components
Speed Settings in Orca Slicer
Speed is one of the most influential factors in 3D printing. It directly impacts print quality, dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and even the overall success rate of your model.
Orca Slicer provides granular speed-control parameters that allow you to optimize everything from the first layer speed to travel movement, overhang behavior, acceleration, jerk control, and extrusion rate smoothing (ERS).
Correctly configuring these speed settings ensures:
✔ Strong first-layer adhesion
✔ Reduced ringing/ghosting
✔ Cleaner overhangs
✔ Better detail on small features
✔ Faster overall print times
✔ Stable extruder flow at high speeds
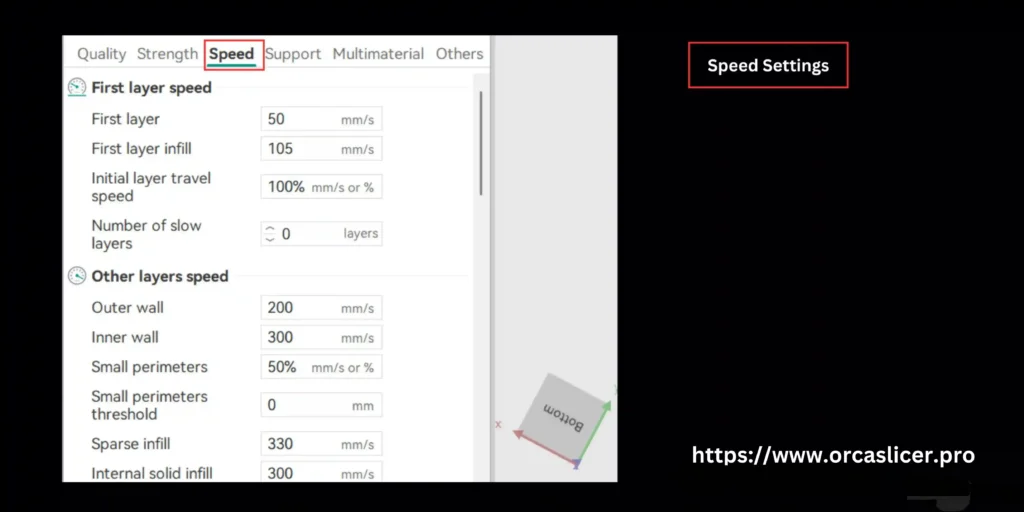
Initial Layer Speed
The initial layer speed controls how fast your printer lays down the very first layer of filament. This layer determines build plate adhesion, so it is intentionally kept slow.
Why it matters:
- Stabilizes the foundation for all other layers
- Ensures strong adhesion to the print bed
- Reduces warping and corner lifting
- Allows the extruded filament to flatten and bond properly
Other Layer Speeds (Main Print Speeds)
Once the first layer is secure, you can define individual speeds for different print regions. Orca Slicer allows advanced control for precision and efficiency.
Includes settings such as
- Includes settings such as:
- Maximum print speed
- Outer wall speed
- Inner wall speed
- Top/bottom solid layer speed
- Gap fill speed
Overhang Speed
Overhangs are areas printed without full support. Orca Slicer automatically slows these based on angle to improve print accuracy.
What controlled overhang speed improves:
- Stronger layer fusion in unsupported regions
- Reduced sagging and drooping
- Cleaner overhang edges
- Better bridging transitions
Travel Speed
Travel speed defines how fast the nozzle moves without extruding filament. This directly affects stringing and surface quality.
Benefits of optimized travel speed:
- Reduces ringing/ghosting when not set too high
- Reduces stringing between parts
- Minimizes blobs caused by oozing
- Cuts overall print time
Acceleration
Acceleration determines how quickly the print head ramps up to speed. Many printers define this in firmware, but Orca Slicer can override it.
Why acceleration control matters:
- Prevents vibrations and ringing on sharp corners
- Improves dimensional accuracy
- Reduces mechanical stress on belts and motors
- Ensures stable movement at high print speeds
Jerk (XY Jerk Control)
Jerk controls how abruptly the printer can change direction without slowing down first.
Optimizing jerk results in:
- Fewer corner artifacts
- Smoother transitions between walls
- Reduced ghosting/ripples
- Better print quality at higher speeds
Advanced Speed Control (Extrusion Rate Smoothing ERS)
High flow-rate printing and rapid acceleration require consistent extrusion changes. Extrusion Rate Smoothing (ERS) prevents pressure fluctuations inside the nozzle.
ERS helps avoid:
- Bulging corners
- Under-extruded edges
- Pressure spikes during sharp direction changes
- Gaps, missing lines, or inconsistent infill
Ideal for:
- Large nozzles (0.6–1.0 mm)
- High-speed flow (200–400 mm/s)
- Input shaping / Klipper-style high-speed printers
Support Settings in Orca Slicer
Support structures play a critical role in stabilizing overhangs, bridges, complex geometries, and unsupported surfaces during 3D printing.
Orca Slicer provides a powerful and flexible suite of support tools, allowing you to fine-tune everything from material usage to support contact points for cleaner, more efficient prints.
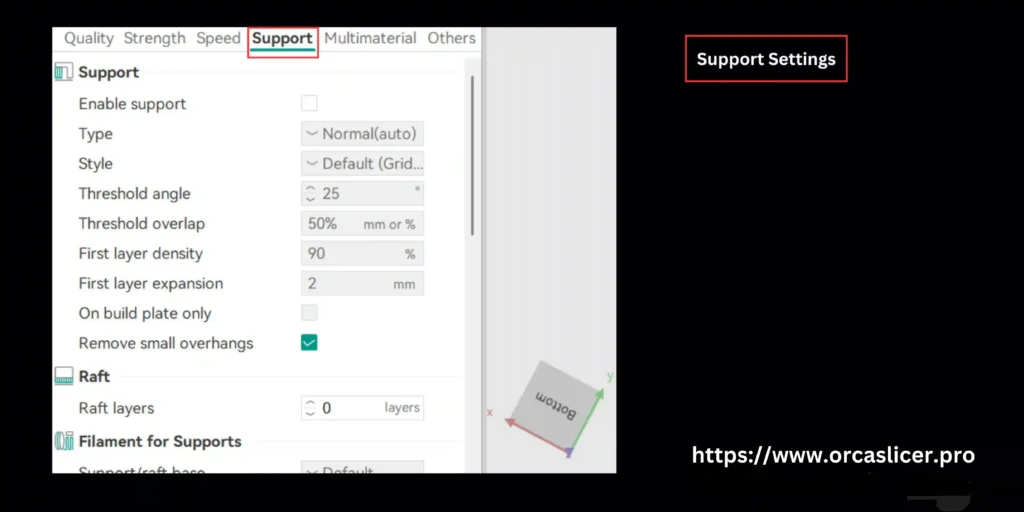
Support (Core Support Structures)
Support structures act as temporary scaffolding for sections of a model that cannot be printed in mid-air. Proper support configuration prevents sagging, layer collapse, and warping in overhanging regions.
Key adjustable parameters:
- Support density
- Support pattern (grid, zig-zag, gyroid, etc.)
- Support overhang threshold
- Interface layers
Raft (Build Surface Assistance)
A raft is a thick, multi-layered base printed underneath the model to enhance bed adhesion and warp resistance.
Benefits of using a raft:
- Helps prints stick to smooth or imperfect build plates
- Reduces warping on large flat-bottom models
- Creates a buffer between the model and the build surface
- Increases success rate for ABS, Nylon, and warp-prone materials
Support Filament (Material & Flow Control)
Support Filament settings give you complete customization over how support material is extruded, ensuring strength while reducing material waste.
What you can configure:
- Base layers (thicker = stronger support foundation)
- Interface layers (smoother separation from the model)
- Support material type (PLA, PETG, breakaway, soluble filament)
- Flow rate & density to balance strength vs. removability
Support Ironing (Surface Finishing for Support Tops)
Support ironing smooths the top layers of the support structure, similar to ironing the top surface of a model.
Benefits of support ironing:
- Creates a clean, flat surface for upper layers to print on
- Reduces artifacts on the underside of overhangs
- Minimizes gaps or rough textures where the model meets the support
- Enhances bridging capability and detail sharpness
Advanced Support Settings
Orca Slicer’s advanced support controls allow precise tuning for challenging models.
Advanced configuration options include:
- Z distance (air gap) for easy removal
- Support wall loops for added stability
- Base pattern spacing
- Support pattern angle
- Layer expansions to widen or shrink support borders
- X/Y offsets for easier detachment
- Adaptive supports (density changes based on model angle)
Tree Supports
Tree supports mimic natural branching structures, minimizing material consumption while supporting complex shapes with curved, angled arms.
Why tree supports are powerful:
- Use significantly less material
- Provide gentle, targeted support for organic and curved models
- Reduce scarring on the model surface
- Extremely easy to remove
Fully customizable parameters include:
- Tip diameter (contact point size)
- Branch diameter
- Branch distance
- Branch density
- Branch angle
- Trunk thickness
- Growth direction
Multimaterial Settings in Orca Slicer
Multimaterial 3D printing allows you to combine different filaments, colors, densities, and mechanical properties within a single model. Orca Slicer provides a robust toolkit to manage material transitions, prevent oozing, stabilize extrusion, and maintain print quality across multiple extruders or material channels.
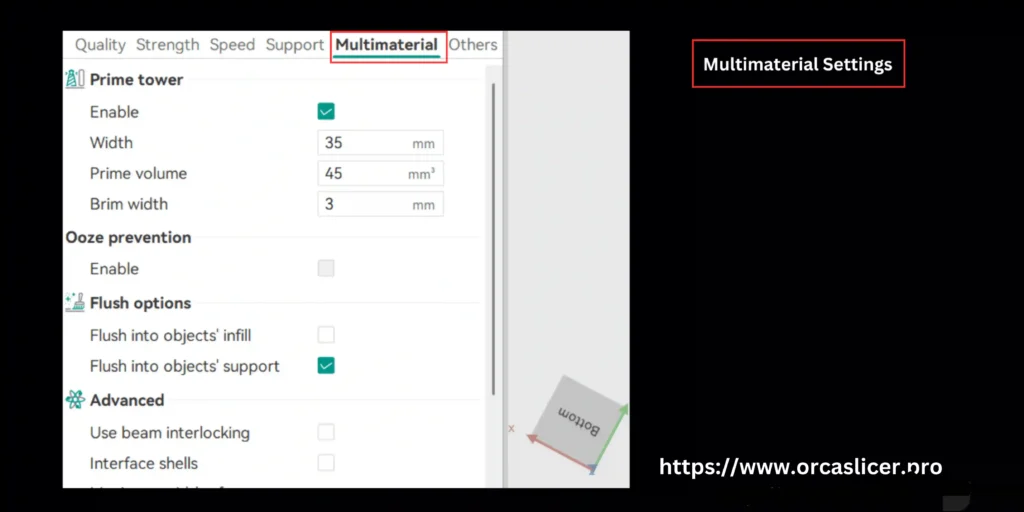
Prime Tower (Stabilizing Material Transitions)
A prime tower is a dedicated structure printed beside the main model to purge old material and stabilize extrusion before switching to a new filament.
Configurable settings include:
- Prime tower size & height
- Extrusion volume before switching
- Tower stability vs. material usage balance
- Placement on the build plate
Filament of Features (Material-Specific Overrides)
When printing with more than one material, each filament may require custom settings for walls, infill, supports, solid layers, or wipe towers.
What you can control:
- Individual wall/perimeter temperatures
- Material-specific infill settings
- Solid infill cooling or extrusion adjustments
- Wipe tower requirements per filament
- Color-by-feature assignment
Ooze Prevention (Controlling Idle Extruders)
Support Filament settings give you complete customization over how support material is extruded, ensuring strength while reducing material waste.
Orca Slicer provides precise ooze-prevention controls such as
- Lowering idle nozzle temperatures
- Preheat timing for reactivation
- Temperature offsets based on filament type
- Automatic cooldown between transitions
Flush Options (Efficient Purging & Nozzle Cleaning)
Flushing (purging) pushes old material out of the nozzle when changing filaments to ensure the next extrusion is clean and accurate.
Key flush settings include:
- Purge volume
- Purge into infill (saves material!)
- Purge lines
- Purge during wipe tower builds
- Partial purge to reduce waste
Advanced Multimaterial Settings (Precision Engineering Control)
Advanced tools allow you to handle complex geometries and tightly integrated multi-material structures.
Advanced settings allow control over:
- Interlocking beams & mechanical joins
- Shell thickness variations for different materials
- Beam direction & density adjustments
- Multilayer depth settings
- Transition layer count
- Support-material alignment
Others Settings in Orca Slicer
The Others Settings tab in Orca Slicer gives you access to additional print-enhancing tools that improve adhesion, surface quality, slicing behavior, and G-Code output. These settings allow you to fine-tune how your printer prepares, executes, and finalizes each print.
Skirt (Stabilizing Extrusion Before Printing)
A skirt is a perimeter printed around your model without touching it to prime the nozzle and prepare the extruder for a smooth first layer.
Why the skirt matters:
- Primes the nozzle for consistent extrusion
- Clears leftover filament before printing the model
- Helps diagnose first-layer issues early
- Stabilizes temperature before the real print starts
Configurable skirt settings include:
- Number of skirt loops
- Distance from the model
- Height of the skirt layers
- Minimum extrusion length
Brim (Boosting First-Layer Adhesion)
A brim is a wide, flat layer printed around the base of your model to improve bed adhesion and reduce warping.
Customizable brim settings:
- Brim width
- Number of brim loops
- Minimum area for brim application
Fuzzy Skin (Textured Surface Generation)
Fuzzy Skin allows you to add a randomized surface texture to your model, giving it a rough or fabric-like finish.
Benefits of Fuzzy Skin:
- Hides visible layer lines and surface defects
- Adds tactile or decorative patterns
- Useful for props, grips, handles, and organic models
Key settings:
- Fuzzy skin thickness
- Randomization amplitude
- Offset and expansion options
Note: It increases printing time and filament usage.
G-Code Output (Controlling File Generation & Compatibility)
G-Code Output settings determine how your G-Code file is structured, which affects printer compatibility, file size, and performance.
You can control:
- Start and end G-Code scripts
- Retraction commands
- Metadata, labeling, and comments
- Travel optimization options
- File formatting for third-party firmware
Why it matters:
- Ensures the file runs perfectly on your specific printer
- Improves readability for troubleshooting
- Optimizes motion paths to reduce artifacts
Post-Processing Scripts (Automation After Slicing)
Post-processing scripts allow you to run custom operations after the G-Code is generated.
Popular use cases:
- Auto-renaming files
- Adding purge macros
- Adding material-specific temperature commands
- Inserting custom cooling or LED controls
- Modifying travel & retraction patterns
Scripts provide advanced control for expert users or custom printer setups
Notes (Personal Instructions & Reminders)
The Notes tab is a simple yet powerful feature for keeping project-specific information.
You can store:
- Print settings reminders
- temperature notes
- filament profiles used
- troubleshooting observations
- version changes or experimental settings
Why it’s helpful:
- Maintains consistency across multiple prints
- Saves time when revisiting complex projects
Prepare Section in Orca Slicer
The Prepare section in Orca Slicer is where your 3D model goes through its initial transformation before slicing. This stage ensures that your design is optimized, correctly formatted, and ready for accurate toolpath generation. Proper preparation directly impacts slicing efficiency, print quality, and overall printer performance.
STL Transformation (From Design to Printable Format)
Orca Slicer primarily works with STL (Standard Tessellation Language) files, which are universally used in FDM 3D printing for defining object geometry using triangular mesh data.
When you import formats like STEP, OBJ, or CAD-based designs, Orca Slicer provides tools to convert them into STL for improved compatibility and slicing accuracy.
What You Can Control
- Why STL Transformation is Important:
- Converts complex CAD models into printable mesh geometry
- Enhances slicing speed and processing efficiency
- Ensures accurate interpretation of curves and surfaces
- Reduces slicing errors and geometry inconsistencies
- Improves layer precision and toolpath calculation
What You Can Do in the Prepare Stage
- Import STEP or OBJ files and convert them to STL
- Rotate, scale, and position models on the build plate
- Detect model orientation issues
- Preview geometry before slicing
- Identify potential printability problems early
Calibrations in Orca Slicer
The Calibration section in Orca Slicer is where you optimize everything that affects print accuracy—temperature, flow, extrusion, and overall material performance. Proper calibration ensures that your printer behaves consistently, produces stable output, and delivers high-quality prints across different materials.
This guide helps you run Orca Slicer’s built-in tests and adjust parameters before starting your final print.
Temperature Calibration
Temperature calibration allows you to fine-tune how your filament melts, flows, and bonds across layers. Since every filament has its own ideal thermal behavior, calibrating these settings ensures consistent extrusion and surface quality.
Why Temperature Calibration Matters
- Prevents stringing, oozing, and blobs
- Improves layer adhesion
- Enhances surface smoothness
- Ensures consistent filament melting
- Reduces under-extrusion and overheating artifacts
What You Can Calibrate
- Nozzle Temperature: Determines melt behavior and extrusion consistency
- Bed Temperature: Controls first-layer adhesion and warping resistance
- Temperature Towers: Enables testing temperature ranges in a single print
- Cooling + Temperature Interaction: Balances heat with cooling fan behavior
- Material-Specific Temps: PLA, PETG, ABS, TPU, ASA, Nylon, CF-filled composites
Benefits of Temperature Calibration
- Improved dimensional accuracy
- Stronger layer bonding
- Fewer print failures
- Better bridging and overhang performance
Flow Rate Calibration
Flow rate determines how much filament your printer extrudes—and even a small miscalibration can cause massive quality issues.
Why Flow Rate Calibration Is Critical
- Under-extrusion → leaves gaps, weak walls, inconsistent layers
- Over-extrusion → causes blobs, elephant foot, dimensional inaccuracies
Finding the correct flow rate ensures your printer deposits exactly the right volume of material for clean, strong, dimensionally accurate prints.
What You Can Adjust
- Global Flow Rate: Overall material extrusion percentage
- First-Layer Flow: Controls how much filament is deposited on Layer 1
- Wall Flow vs. Infill Flow: Balance structural strength and smooth surfaces
- Flow for Bridging: Ensures sag-free bridges
- Extrusion Multiplier: Fine micro-adjustment for precise filament volume
Results of Correct Flow Calibration
- Strong, solid prints without weak spots
- Smooth wall surfaces
- Accurate dimensions
- Clean infill patterns
- No underfilled layers or overflowing material
Pressure Advance
Pressure Advance is a calibration technique that stabilizes extrusion by compensating for the pressure changes inside your nozzle. As the print head speeds up, slows down, or changes direction, the internal filament pressure shifts and without correction, this causes blobs, zits, oozing, corner bulges, and inconsistent line widths.
Pressure Advance helps the printer predict these pressure highs and lows and adjust extrusion in real time for clean, accurate prints.
Adaptive Pressure Advance
Adaptive Pressure Advance is an enhanced calibration mode that automatically adjusts extrusion pressure based on the toolhead’s movement. Instead of applying a fixed value, it intelligently adapts the pressure for different speeds, accelerations, and printing scenarios.
This results in cleaner corners, smoother walls, accurate bridges, and consistent extrusion across complex geometries.
What Adaptive Pressure Advance Does
- Dynamically compensates for pressure fluctuations
- Adjusts extrusion behavior during acceleration & deceleration
- Balances flow rate for sudden speed changes
- Ensures cleaner transitions in high-speed printing
Why It Matters
Adaptive Pressure Advance improves print quality by managing:
- Flow rate stability
- Corner sharpness
- Overhang and bridge accuracy
- Surface consistency on high-detail areas
- Speed-based extrusion variations
Retraction
Retraction settings control how the filament is pulled back into the nozzle during non-printing movements. By dialing in these parameters correctly, you can significantly reduce stringing, oozing, blobs, zits, and residual extrusion artifacts—especially in models with frequent travel moves or fine details.
What Retraction Settings Control
- Filament pullback distance
- Retraction speed
- Priming (push-forward) after retraction
- Nozzle pressure during travel
- Extrusion restart behavior
Why Retraction Matters
Correct retraction tuning ensures:
- Clean transitions between printed features
- Zero or minimal stringing across gaps
- Reduced blobs at start/stop points
- Stable nozzle pressure during movement
- Better detail accuracy on multi-part geometries
Retraction Testing (Before Final Printing)
Orca Slicer allows you to run dedicated retraction tests to find your ideal values. These tests help you evaluate:
- Optimal retraction length
- Best retraction speed
- Amount of required priming
- Impact on thin walls & intricate shapes
- Temperature + retraction interaction
Tolerance
Tolerance settings help you fine-tune how accurately your printed parts match the intended dimensions. Even if you use the same STL file, same slicer profile, and the same filament spool, dimensional variations can still occur due to differences in mechanics, extrusion systems, nozzle wear, material shrinkage, and printer calibration.
Orca Slicer solves this by offering printer-specific tolerance controls, allowing every machine in your setup to achieve precise and repeatable dimensions.
What Orca Slicer Lets You Adjust
- XY compensation
- Hole compensation
- Shrinkage correction
- Scaling adjustments
- Offset tuning for mechanical fit
- Dimensional flow correction
Advanced Calibration
In this section, you can fine-tune advanced calibration parameters that directly impact extrusion consistency, motion accuracy, vibration control, and overall print quality.
Volumetric Speed
Volumetric speed defines the maximum amount of filament (mm³/s) your extruder can melt and push through the nozzle. This setting is crucial because every material whether PLA, PETG, ABS, TPU, or composite filaments has a different melt flow capacity. Tuning volumetric speed properly ensures smooth extrusion, consistent layer deposition, and stable print quality.
What Volumetric Speed Optimization Helps You Achieve:
- Avoid Nozzle Clogs
Prevents the hotend from being overloaded with molten filament, reducing the chances of jams and heat creep. - Stop Under-Extrusion
Ensures the nozzle always delivers enough material, eliminating weak layers, gaps, or missing sections in your model. - Prevent Over-Extrusion
Controls excess filament output, avoiding blobs, zits, elephant skin, and dimensionally inaccurate prints. - Improve Layer Adhesion
Maintains the ideal material flow needed for each layer to bond properly, improving overall durability and print strength. - Optimize Material Throughput
Helps your printer maintain consistent flow rates when working with different nozzle sizes, material types, and high-speed printing conditions.
Cornering (Jerk & Junction Deviation)
Cornering settings control how your 3D printer behaves when transitioning through sharp corners, curves, and directional changes. These parameters Jerk and Junction Deviation directly influence print smoothness, dimensional accuracy, vibration levels, and extrusion stability.
What Proper Cornering Calibration Helps You Optimize:
- Higher Speed With Better Control: Allows you to push travel and print speeds without sacrificing precision ideal for Orca Slicer’s high-speed profiles.
- Sharper & Cleaner Corners
Prevents rounded edges, ringing, and overshoot by ensuring the toolhead transitions smoothly at direction changes. - Consistent Extrusion at Turns
Regulates filament flow during sudden speed shifts, eliminating blobs, zits, and under-extruded corners. - Reduced Mechanical Vibrations
Minimizes shaking caused by abrupt toolhead movement, improving surface quality and print stability. - Improved Dimensional Accuracy
Helps the printer follow the model’s exact geometry, especially for functional prints, joints, brackets, and mechanical parts. - Smoother Curves & Arcs
Maintains balanced motion so curves appear fluid without visible stepping or micro-ringing.
Input Shaping
Input Shaping is a powerful motion-control feature that reduces mechanical vibrations generated during fast movements of the toolhead. These vibrations often seen as ringing, ghosting, or echoing appear on vertical walls of the print. With proper Input Shaping calibration, you can print faster, smoother, and cleaner without compromising quality.
What Input Shaping Helps You Optimize:
- Cleaner Curves & Detailed Surfaces: Removes vibration artifacts, helping functional parts and aesthetic prints achieve a premium finish.
- Eliminate Ringing/Ghosting
Cancels out oscillations caused by rapid directional changes, giving your prints crisp edges and smooth walls. - Higher Print Speeds With Stability
Enables the printer to move significantly faster while maintaining surface quality—ideal for high-speed slicer profiles. - Reduced Mechanical Stress
Softens acceleration peaks, preventing wear on belts, motors, bearings, and the frame. - Improved Dimensional Accuracy
Ensures corners, holes, and structural features maintain their exact shape even during fast toolhead movements. - Better Flow Consistency
Stabilizes nozzle movement so extrusion remains smooth, reducing surface unevenness or micro-defects.
VFA (Vertical Fine Artifacts)
Vertical Fine Artifacts (VFA) are small imperfections or micro-defects that appear along vertical walls, corners, and surfaces of your 3D print. They usually occur due to sudden direction changes, inconsistent extrusion, or minor vibrations, affecting both aesthetic and dimensional quality. Orca Slicer provides built-in settings to detect, reduce, and prevent VFA, ensuring smooth, high-quality prints.
What VFA Settings Help You Optimize:
- Smooth Vertical Surfaces
Reduces tiny bumps, lines, and streaks along walls and pillars for professional-grade finishes. - Improve Dimensional Accuracy
Corrects imperfections at sharp corners and sudden directional changes, preserving model fidelity. - Enhance Surface Consistency
Ensures consistent layer stacking, preventing gaps or misalignments in vertical features. - Minimize Artifacts from Speed or Acceleration
Works with speed, acceleration, and jerk settings to control unwanted filament shifts. - Better Finish for Functional and Decorative Prints
Ideal for mechanical parts, detailed models, or display-quality prints where smoothness matters. - Integrated Orca Slicer Controls
Adjust directly within Orca Slicer without needing external plugins or complex tuning.
Orca Slicer is a powerful, versatile, and user-friendly 3D printing slicer designed to optimize every aspect of your printing workflow from printer configuration and material settings to process calibration and advanced motion control.
Whether you are a beginner learning to set up your first print or an expert fine-tuning high-speed, multi-material projects, Orca Slicer provides precise control over printer parameters, filament behavior, speed, supports, and surface quality.
By mastering its extensive settings including printer calibration, layer height, infill patterns, speed optimization, support structures, multimaterial management, and advanced features like Input Shaping, Cornering, Volumetric Speed, and VFA you can achieve high-quality, reliable, and aesthetically flawless 3D prints.
With Orca Slicer, every user can unlock the full potential of their 3D printer, reducing print failures, improving surface finish, and ensuring consistent dimensional accuracy across all projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I calibrate filament flow in Orca Slicer to avoid over- or under-extrusion?
Use the built-in Flow Rate calibration tool. Print the flow test blocks (or calibration cube) at varying flow modifiers, inspect which gives the smoothest, most consistent layer surface, then update the filament’s flow ratio accordingly.
Start with a conservative flow value (often default ~ 1.0).
Test increments (e.g. +5%, –5%).
Re-slice and check results: if top layers are thin or gaps appear → increase flow; if blobs or bulging → lower flow.
How can I eliminate stringing or oozing between print moves?
Properly configure Retraction settings — set a suitable filament pull-back distance and retraction speed, and combine this with optimal temperature and travel settings.
Use the built-in Orca retraction test to find best values
Lower nozzle temperature slightly if filament remains too liquid.
Increase travel speed so the nozzle spends less time traveling across gaps
My prints show ripples or “ghosting” on vertical walls – how do I fix that?
This often comes from vibrations and rapid acceleration/jerk during directional changes. In Orca Slicer, reducing acceleration/jerk or enabling Input Shaping helps minimize these artifacts.
Lower acceleration / jerk values gradually.
Enable Input Shaping (if supported by your firmware/hardware) to cancel vibrations during high-speed movement.
Check frame rigidity — loose belts or shaky frame magnify ringing issues.
How do I find the right settings when switching filament types (PLA → PETG → ABS)?
Whenever you change filament type you should re-run key calibrations: temperature tower, flow calibration, retraction test and optionally pressure advance / volumetric tests. This ensures extrusion behavior and layer adhesion are optimized for new material.
Print a temperature tower to check best nozzle & bed temperature.
Run flow calibration.
Retest retraction if filament viscosity differs.
If using advanced features (Input Shaping, high-speed printing), re-evaluate volumetric speed and pressure advance.
Can I print high-speed while maintaining quality – what settings matter?
Yes — but you need careful calibration. Key settings: volumetric speed, acceleration/jerk, pressure advance/input shaping, retraction, travel speed. In Orca Slicer you can test maximum volumetric speed and vibration compensation to balance speed and quality.
Find max safe volumetric speed that doesn’t cause under-extrusion or clogging
Enable Input Shaping or reduce jerk/acceleration to avoid ringing.
Use stable retraction and flow settings to avoid extrusion glitches at high speeds.
My mechanical parts don’t fit well – holes too tight or loose. How to fix?
Use the Tolerance / Dimensional Calibration features in Orca Slicer. Print a calibration cube or tolerance test model (holes, slots, etc.), measure actual dimensions, then adjust tolerance settings or flow/scale compensation to match the design
Always calibrate whenever you change nozzle, filament, or significantly alter print speed/material.
Overhangs or bridges look poor even with supports — what can I tweak?
Check a combination of settings: support settings (support density, interface layers, Z-gap), cooling fan behavior, and extrusion flow. Insufficient support or incorrect support interface often leads to sagging or poor quality.
Increase support interface density or reduce support wall spacing.
Optimize support-to-model distance for easy removal.
Ensure proper cooling for bridging segments; reduce layer height for better bridging.




